Salbutamol, also known as Albuterol and is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs. It is used to treat asthma including asthma attacks, exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It may also be used to treat high blood potassium levels. Salbutamol is usually used with an inhaler or nebulizer but is also available as a pill and intravenous solution. Onset of action of the inhaled version is typically within 15 minutes and lasts for two to six hours.
Molecular Structure |
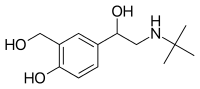
Class of Drug |
β-adrenergic agonist, bronchodilator.
Mechanism of Action |
Relaxes smooth muscles of the bronchioles by stimulating β-adrenergic receptors.
Indications / Dosage / Route |
Routes of Administration: Oral and inhalation.
Condition: Bronchodilation
Dose: Adults, children >12 years: 2 inhalations q4-6h.
Condition: Prophylaxis of exercise-induced bronchospasm
Dose: Adults, children >12 years: 2.5 mg t.i.d. to q.i.d. by nebulization.
Condition: Bronchodilation: Capsule for inhalation
Dose: Adults, children >12 years: 200 pg q4-6h.
Condition: Prophylaxis of exercise-induced bronchospasm
Dose: Adults, children>12 years: 200 pg 15 minutes before exercise.
Condition: Bronchodilation: syrup
Dose: Adults, children >14 years: 2-4 mg t.i.d. to q.i.d.
Children: 2-6 years: Initial: 2-4 mg, Maximum: 8 mg ti.d. to q.i.d.
Children 6-12 years: 4 mg ql2h. Maximum: 12 mg ql2h.
Elderly Initial: 2 mg t.i.d. to q.i.d. Increase dose if needed to maximum of 8 mg ti.d. to q.i.d.
Condition: Bronchodilation: extended-release tablets
Dose: Adults, children >12 years: 4-8 mg ql2h. Maximum: 32 mg/d.
Adjustment of Dosage |
Kidney disease: None.
Liver disease: None.
Elderly: See above
Pediatric: See above
| Onset of Action | Duration | |
| <30 min <5 min | Inhalation Oral | 4-8 h 3-8 h |
Food and Drug Interactions |
Food: Not applicable.
Pregnancy: Category C.
Lactation: No data available. Other drugs in the same class such as terbutaline are considered compatible with breastfeeding.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to adrenergic compounds.
Warnings / Precautions |
> Use with caution in patients with the following conditions: hyperthyroidism, diabetes, coronary insufficiency, ischemic heart disease, history of stroke, CHE, hypertension.
> Some preparations contain bisulfite, which may cause an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals.
> Instruct patient in proper technique for using nebulizer and/or inhaler.
Clinically Important Drug Interactions |
> Drugs that increase effects/toxicity of β agonists: inatropium, MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants.
> Drugs that decrease activity of beta agonists: sympathomimetic drugs (nasal decongestants, weight loss drugs, eg, phenylpropa-nolamine), anticholinergic drugs, phenothiazines.
Adverse Reactions |
> Common: tremor.
> Serious: hypotension, bronchospasm.
Parameters to Monitor |
> Monitor patient for possible development of tolerance with prolonged use. Discontinue drug temporarily and effectiveness will be restored.
> Signs of paradoxical bronchospasm.
> Pulmonary function on initiation and during bronchodilator therapy. Assess respiratory rate, sputum character (color, quantity), peak airway flow, 02 saturation and blood gases.
> Efficacy of treatment: Improved breathing, prevention of bronchospasm, reduction of asthmatic attacks, prevention of exercise-induced asthma. If no relief is obtained from 3-5 aerosol inhalations within 6-12 hours, reevaluate effectiveness of treatment.
> FEV1 rate to determine effectiveness of the drug to reverse bronchostriction. Efficacy is indicated by an increase in FEV1 of 10-20%. In addition such patients, as well as those who have chronic disease, should be given a peak flow gauge and told to determine peak expiratory flow rate at least twice daily.
Advice to Patient |
> Avoid OTC products without consulting treating physician.
> Do not use solutions that contain a precipitate or are discolored.
> Contact treating physician if more than 3 inhalations are required within a 24-hour period to obtain relief.
> Wait at least 1 minute after 1 or 2 inhalations before taking a third dose.
> Keep spray away from eyes.
> Maintain adequate fluid intake (2000-3000 mL/d) to facilitate clearing of secretions.
> Rinse mouth with water after each inhalation to minimize dry mouth and throat irritation.
> Administer inhalant when arising in the morning and before meals.
> Do not increase dose in an attempt to obtain relief.
Further Useful Info |
> For patients with acute asthma or acute exacerbation of COPD, reduce dose to minimum necessary to control condition after initial relief is achieved. For chronic conditions, the patient should be reassessed every 1-6 months following con¬trol of symptoms.


