Ofloxacin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections like pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infections, prostatitis, plague and certain types of infectious diarrhea. Other uses of ofloxacin, along with other medications, include multidrug resistant tuberculosis. An eye drop of ofloxacin may be used for a superficial bacterial infection of the eye and an ear drop may be used for otitis media when there is a hole in the ear drum.
Molecular Structure |
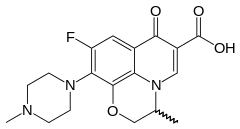
Class of Drug |
Broad-spectrum quinolone antibiotic.
Mechanism of Action |
Inhibits DNA gyrase, there by blocking bacterial DNA replication.
Susceptible organisms in vivo: Citrobacter sp, Enterobacter sp, Escherichia coli, Hemophilus ducreyi, Hemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus. Limited activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes.
Indications / Dosage / Route |
Routes of Administration: Oral, IV(same doses by both routes), topical (ophthalmic).
Condition: Acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, community acquired pneumonia, uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections
Dose: Adults: 400 mg q12h, 10 days.
Condition: Acute uncomplicated urethral and cervical gonorrhea
Dose: Adults: 400 mg, single dose, 1 day.
Condition: Nongonococcal cervicitis/urethritis, mixed infection of urethra and cervix
Dose: Adults: 300 mg q12h, 7 days.
Condition: Acute pelvic inflammatory disease, uncomplicated cystitis (E. coli, K. pneumoniae, other approved pathogens), complicated UTIs
Dose: Adults: 200 mg q12h, 3-10 days.
Condition: Prostatitis (E. coli)
Dose: Adults 300 mg q12h, 6 weeks.
Condition: Conjunctivitis
Dose: Adults: Ophthalmic solution (0.3%): Initial: 1-2 drops in affected eye(s) q2-4h, first 2 days. Then 1-2 drops q.i.d. for 5 additional days.
Adjustment of Dosage |
Kidney disease: Creatinine clearance 10-50 mL/min: dosage interval: 24 hours; creatinine clearance <10 mL/min: one-half dosage q24h.
Liver disease: None.
Elderly: None
Pediatric: Safety and efficacy have not been established in children <18 years.
Food and Drug Interactions |
Food: Take 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals with a glass of water.
Pregnancy: Category C.
Lactation: Appears in breast milk. Potentially toxic to infant. Avoid breastfeeding.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolone antibiotics or quinolone antibiotics, eg, cinoxacin, nalidixic acid.
Warnings / Precautions |
> Use with caution in patients with CNS disorders (epilepsy), kidney disease.
> Therapy should be continued for 2-4 days after symptoms have disappeared.
> Achilles and other tendon rupture have occurred in patients taking fluoroquinolones.
> Serious and fatal hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with these drugs, even after the first dose.
> Reserve use of this drug for infections that are difficult to treat by other means.
Clinically Important Drug Interactions |
> Drugs that increase effects/toxicity of fluoroquinolones: cyclosporine, probenecid.
> Dmgs that decrease effects/toxicity of fluoroquinolones: antacids, antineoplastic agents, didanosine, sucralfate, iron salts, zinc salts, caffeine.
> Fluoroquinolones increase effects/toxicity of oral anticoagulants, theophylline, caffeine.
Adverse Reactions |
> Common: None.
> Serious: hypersensitivity reaction (anaphylaxis), seizures, pseudomembranous colitis, cholestatic jaundice, renal failure, pulmonary edema, pulmonary embolism, cardiovascular col-lapse, pharyngeal edema.
Parameters to Monitor |
> Renal, hepatic, and hemopoietic systems should be monitored periodically during prolonged therapy.
> Intake of fluids and urinary and other fluid output to minimize renal toxicity. Increase fluid intake if inadequate. Closely monitor electrolyte levels.
> Signs of hypersensitivity reactions.
> Signs and symptoms of antibiotic induced bacterial or fungal superinfection: Use of yogurt (4 oz/d) may be helpful in prevention of superinfection.
> Signs and symptoms of tendon pain. These may be an indication of tendon rupture.
> Monitor patients for evidence of development of microbial resistance with loss of effectiveness.
Advice to Patient |
> Limit intake of caffeinated products including coffee and colas.
> Drink a great deal of fluids during therapy with this drug.
> Do not undertake strenuous exercise while taking this drug.
> To minimize possible photosensitivity reaction, apply adequate sunscreen and use proper covering when exposed to strong sunlight.
Further Useful Info |
> Ofloxacin offers no advantages over ciprofloxacin, but is less active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
> Levofloxacin (an Lisomer of ofloxacin) is much more effective against gram-positive organisms.
> Use of Ofloxacin is limited to treatment of UTI, prostatitis, and uncomplicated gonorrhea.
> This drug is recommended as an alternative to aminoglyco-sides when clinically relevant.


