Furosemide is a medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken intravenously or by mouth. When taken by mouth it typically begins working within an hour while intravenously
Molecular Structure |
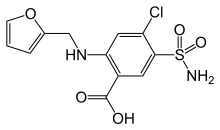
Class of Drug |
Loop diuretic.
Mechanism of Action |
Inhibits sodium and chloride reabsorption in proximal part of ascending loop of Henle.
Indications / Dosage / Route |
Routes of Administration: Oral, IV and IM.
ORAL
Condition: Edema
Dose: Adults: Initial: PO 20-80 mg/d as single dose. Increase by 20-40 mg q6-8h pm. Maximum: 600 mg/d.
Children: Initial: PO 2 mg/kg as single dose. Increase by 1-2 mg/kg q6-8h pm. Maximum: 6 mg/kg.
Condition: Hypertension
Dose: Adults: Initial: PO 40 mg b.i.d.
Condition: CHF, chronic renal failure
Dose: Adults: PO 2-2.5 g/d.
Condition: Hypercalcemia
Dose: Adults: PO 120 mg/d in 1-3 doses.
IV and IM
Condition: Edema
Dose: Adults: Initial: IV, IM 20-40 mg. Increase dose in 20-mg increments if needed.
Children: Initial: IV, IM 1 mg/kg. After 2 hours, increase dose by 1 mg/kg if needed. Maximum: 6 mg/kg.
Condition: Hypercalcemia
Dose: Adults: IV, IM 80-100 mg. Repeat q1-2h.
Condition: Acute pulmonary edema
Dose: Adults: IV 40 mg over 1-2 min if needed. Give 80 mg over 1-2 min after 1 hour.
Condition: CHF, chronic renal failure
Dose: Adults: IV 2-2.5 g/d. Maximum: 1 g/d over 30 min.
Condition: Hypertensive crisis, normal renal function
Dose: Adults: IV 40-80 mg.
Condition: Hypertensive crisis with pulmonary edema or acute renal failure
Dose: Adults: IV 100-200 mg
Adjustment of Dosage |
Kidney disease: May require higher dosage. See Warnings/ Precautions.
Liver disease: Use with caution. At higher risk for toxicity.
Elderly: Use with caution. At higher risk for toxicity.
Pediatric: See above.
| Onset of Action | Peak Effect | Duration | |
| Oral IV | Within 60 min Within 5 min | 60-120 min 30 min | 6-8 h 2 h |
Food and Drug Interactions |
Food: Take with food or milk.
Pregnancy: Category C.
Lactation: Appears in breast milk. Potentially toxic to infants. Best to avoid.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to sulfonamides, anuria, hepatic coma, severe electrolyte depletion
Warnings / Precautions |
> Use with caution in patients with the following conditions: hepatic cirrhosis, depressed renal function, elderly.
> Generally requires concomitant potassium supplementation. May require addition of aldosterone antagonist.
> Systemic lupus erythematosis may be exacerbated by the drug.
> May cause ototoxicity, especially in setting of renal insufficiency, if recommended doses are exceeded or when given with other ototoxic agents.
> Administer drug in the morning so as to promote diuresis before bedtime. Consider magnesium supplement for all patients receiving large doses of the drug IV for acute CHF.
> Hepatic encephalopathy and coma may be precipitated in patients with cirrhosis.
> Hypokalemia may be particularly serious in patients who are taking digitalis or have potassium losing nephropathy or history of ventricular arrthymias.
> If serum potassium is <3.5 meq/L, consider addition of potassium sparing diuretic.
Clinically Important Drug Interactions |
> Drugs that increase effects/toxicity of loop diuretics: other nephrotoxic or ototoxic drugs, amphotericin B, steroids.
> Drugs that decrease effects/toxicity of loop diuretics: probenecid, indomethacin, potassium-sparing diuretics.
> Loop diuretics increase levels/toxicity of the following: lithium.
> Loop diuretics potentiate hypotensive effects of other diuretics, most antihypertensive drugs.
Adverse Reactions |
> Common: dizziness.
> Serious: orthostatic hypotension, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, alkalosis, renal insufficiency, pancreatitis, hepatitis, bone marrow suppression, hearing loss, kidney stones.
Parameters to Monitor |
> Serum electrolytes (K, Na, Cl, bicarbonate, Ca, Mg, uric acid).
> CBC with differential and platelets.
> Efficacy of treatment: ideal weight loss of 0.3-1 kg/d, urine output >300-1000 mL/d over normal daily output.
> Signs of severe hypotension for patients with severe mitral or aortic stenosis. Ischemia may result.
> Liver function for patients in hepatic failure.
> Signs of oliguria. Consider discontinuation of therapy if persistent >24 hours.
> Symptoms of dehydration.
> Signs and symptoms of ototoxicity: tinnitus, vertigo, hearing loss, initially in range of4000-8000 Hz. Irreversible deafness may occur in this setting.
> Signs and symptoms of renal toxicity.
> Signs and symptoms of bone marrow depression.
> Signs and symptoms of too vigorous diuresis: rapid weight loss, acute fall in BP. In elderly the following symptoms may occur: lightheadedness, dizziness, vomiting, muscle cramps, bladder spasm, urinary frequency.
> Signs of hyperglycemia particularly in diabetics.
> Intake of fluids and urinary and other fluid output. Increase fluid intake if inadequate to minimize renal toxicity.
Advice to Patient |
> Change position slowly, in particular from recumbent to upright, to minimize orthostatic hypotension. Sit at the edge of the bed for several minutes before standing, and lie down if feeling faint or dizzy. Avoid hot showers or baths and standing for long periods. Male patients should sit on the toilet while urinating rather than standing.
> To minimize possible photosensitivity reaction, apply adequate sunscreen and use proper covering when exposed to strong sunlight.
> Do not stand in one position for a prolonged period.
> Use caution when taking hot baths or showers and when performing strenuous exercise in hot weather.
> Supplement diet with potassium rich foods: bananas, citrus fruit, peaches, dates.
Further Useful Info |
> Oral furosemide is the drug of first choice for therapy for fluid overload states caused by mild to moderate heart failure.
> Furosemide is considered to be a secondary drug for treatment of ascites associated with hepatic cirrhosis if spironolactone has not controlled the edema.


