This discussion includes the following information related to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or Polycystic Ovary Disease (PCOD)
- Signs and Symptoms of PCOS
- Causes of PCOS
- Complications of Polycystic Ovary Disease
- Tests and Diagnosis for PCOD
- Treatment and Drugs for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Definition
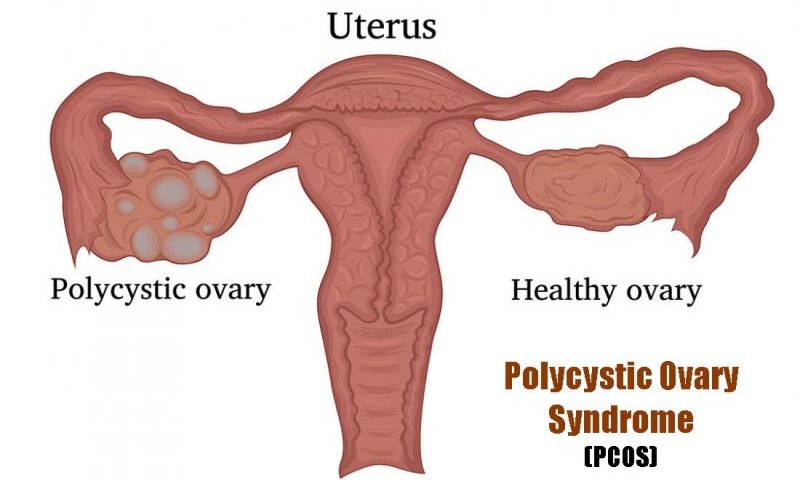
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine system disorder among women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have enlarged ovaries that contain small collections of fluid — called follicles — located in each ovary as seen during an ultrasound exam.
Infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods, excess hair growth, acne, and obesity can all occur in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. In adolescents, infrequent or absent menstruation may raise suspicion for the condition.
The exact cause of polycystic ovary syndrome is unknown. Early diagnosis and treatment along with weight loss may reduce the risk of long-term complications, such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Signs and Symptoms of PCOS / PCOD
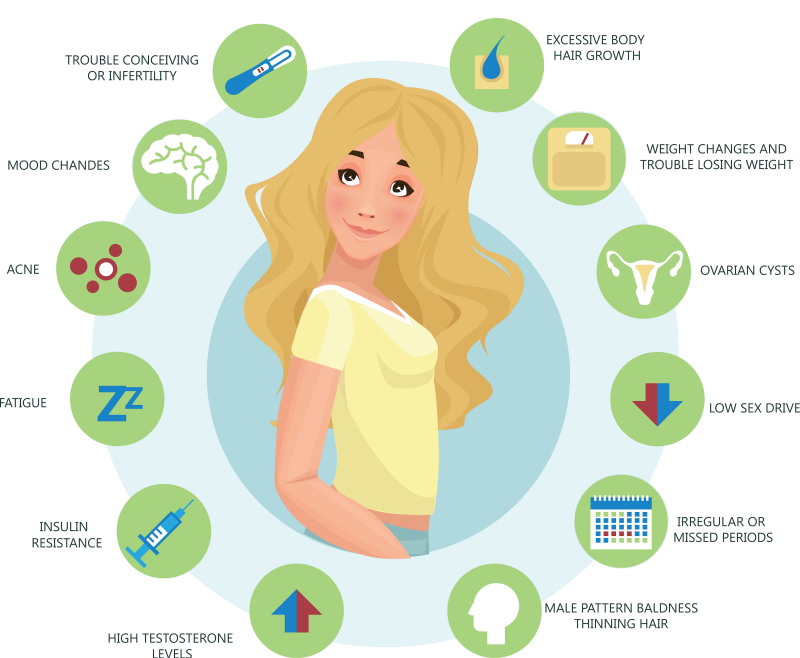
Polycystic ovary syndrome signs and symptoms often begin soon after a woman first begins having periods (menarche). In some cases, PCOS develops later during the reproductive years, for instance, in response to substantial weight gain.
PCOS has many signs — things you or your doctor can see or measure — and symptoms — things that you notice or feel. All of these can worsen with obesity. Every woman with PCOS may be affected a little differently.
To be diagnosed with the condition, your doctor looks for at least two of the following:
- Irregular Periods: This is the most common characteristic. Examples include menstrual intervals longer than 35 days; fewer than eight menstrual cycles a year; failure to menstruate for four months or longer; and prolonged periods that may be scant or heavy.
- Excess Androgen: Elevated levels of male hormones (androgens) may result in physical signs, such as excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), adult acne or severe adolescent acne, and male-pattern baldness (androgenic alopecia).
- Polycystic Ovaries: Polycystic ovaries become enlarged and contain numerous small fluid-filled sacs which surround the eggs.
EMERGENCY CASE See your doctor if you have concerns about your menstrual periods, if you’re experiencing infertility or if you have signs of androgen excess such as acne and male-pattern hair growth.
Causes of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
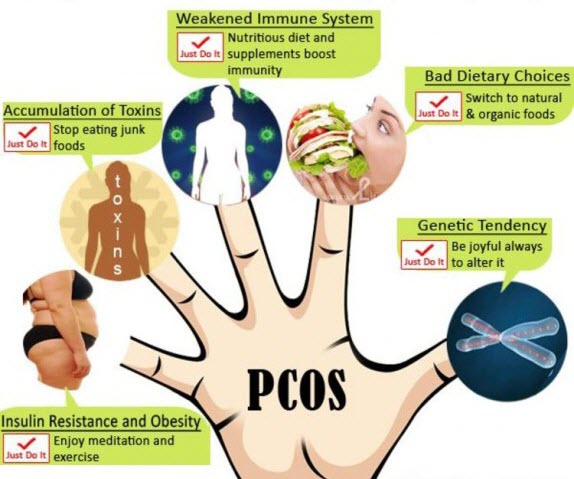
Doctors don’t know what causes polycystic ovary syndrome, but these factors may play a role:
- Excess Insulin: Insulin is the hormone produced in the pancreas that allows cells to use sugar (glucose) — your body’s primary energy supply. If you have insulin resistance, your ability to use insulin effectively is impaired, and your pancreas has to secrete more insulin to make glucose available to cells. Excess insulin might also affect the ovaries by increasing androgen production, which may interfere with the ovaries’ ability to ovulate.
- Low-Grade Inflammation: Your body’s white blood cells produce substances to fight infection in a response called inflammation. Research has shown that women with PCOS have low-grade inflammation and that this type of low-grade inflammation stimulates polycystic ovaries to produce androgens.
- Heredity: If your mother or sister has PCOS, you might have a greater chance of having it, too. Researchers also are looking into the possibility that certain genes are linked to PCOS.
Complications of Polycystic Ovary Disease
Having polycystic ovary syndrome may make the following conditions more likely, especially if obesity also is a factor:
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Cholesterol and lipid abnormalities, such as elevated triglycerides or low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol
- Metabolic syndrome — a cluster of signs and symptoms that indicate a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis — a severe liver inflammation caused by fat accumulation in the liver
- Infertility
- Sleep apnea
- Depression and anxiety
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Cancer of the uterine lining (endometrial cancer), caused by exposure to continuous high levels of estrogen
- Gestational diabetes or pregnancy-induced high blood pressure