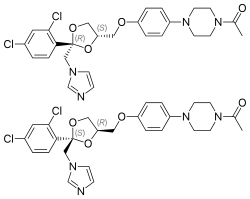
Ketoconazole is a synthetic imidazole antifungal drug used primarily to treat fungal infections. Ketoconazole is sold commercially as a tablet for oral administration, and in a variety of formulations for topical administration, such as creams (used to treat tinea; cutaneous candidiasis, including candidal paronychia; and pityriasis versicolor) and shampoos (used primarily to treat dandruff seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp).
Molecular Structure |
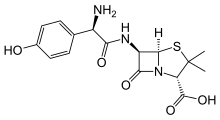
Class of Drug |
Antibiotic, penicillin family, aminopenicillin.
Mechanism of Action |
Inhibits synthesis of steroids in fungal cell membranes, resulting in leakage of essential cellular components
Susceptible organisms in vivo: Candida sp, Cryptococcus, Coccidioides, Histoplasma, Blastomyces.
Indications / Dosage / Route |
Routes of Administration: Oral only.
Condition: Systemic fungal infections
Dose: Adults: 200 mg once daily. Increase to 400 mg once daily if needed.
Children >2 years 3.3-6.6 mg/kg once daily
Adjustment of Dosage |
Kidney disease: None
Liver disease: None.
Elderly: None
Pediatric: Safety and efficacy in children <2 years have not been established.
Food and Drug Interactions |
Food: Should be taken with food, especially citrus juices.
Pregnancy: Category C.
Lactation: Probably present in breast milk. Avoid breastfeeding.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ketoconazole or other azole antifungals, concomitant astemizole, triazolam.
Warnings / Precautions |
> Treatment of candidiasis requires 1-2 weeks; for other systemic mycoses, 6 months.
> Do not administer along with astemizole or other azoles.
Clinically Important Drug Interactions |
> Ketoconazole increases effects/toxicity of hepatotoxic drugs, cisapride, oral anticoagulants, astemizole, cyclosporine, astemizole, corticosteroids, midazolam, triazolam.
> Ketoconazole decreases effects/toxicity of theophylline.
> The following drugs decrease effects/toxicity of ketoconazole: antacids (containing calcium, aluminum), anticholinergics, rifampin, isoniazid.
Adverse Reactions |
> Common: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain
> Serious: hepatotoxicity.
Parameters to Monitor |
> Signs and symptoms of liver toxicity.
Advice to Patient |
> Take antacids, if needed, 2 hours after this drug. The same is true for other drugs that decrease gastric activity, eg, H2 blockers.
> Report symptoms of possible liver dysfunction: jaundice, anorexia, dark urine, pale stools, nausea, vomiting.
> Avoid driving and other activities requiring mental alertness or that are potentially dangerous until response to drug is known.
> Avoid alcohol.
> To minimize possible photosensitivity reaction, apply adequate sunscreen and use proper covering when exposed to strong sunlight.
Further Useful Info |
> Ketoconazole is effective in non-CNS infections caused by Candida, blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, and coccidiomycosis.
> Problems with oral absorption occur, especially in patients with AIDS, neutropenic patients, or patients on antacids or other acid-blocking agents.
> This drug should not be used in cryptoccal infections. Fluconazole should be substituted.