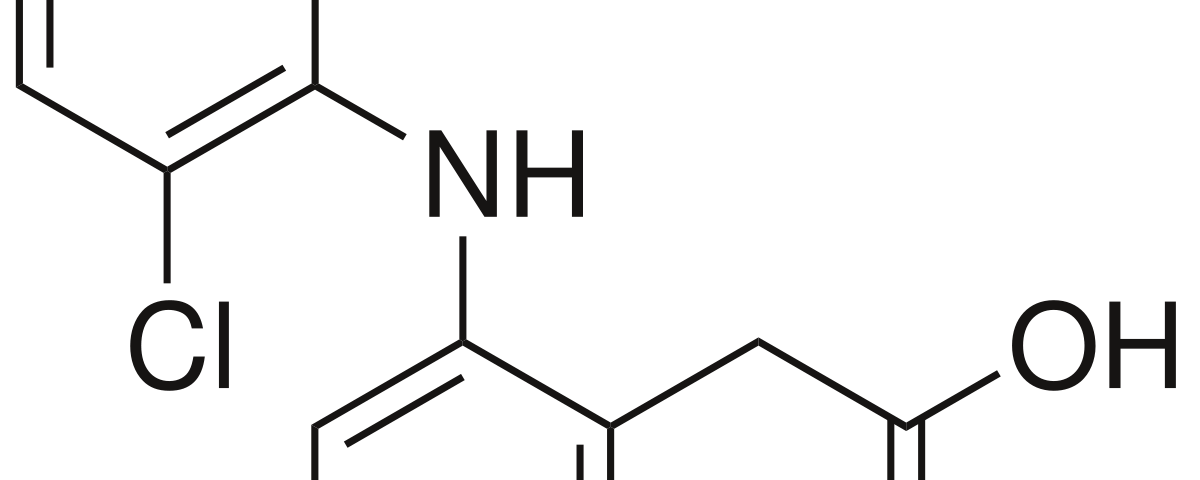
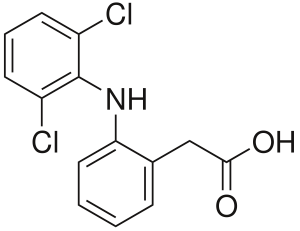
Diclofenac is a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID) which is most commonly used for reducing Inflammation. It also serves as Analgesic and used to treat pain in certain conditions.
Molecular Structure |
Class of Drug |
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)
Mechanism of Action |
Inhibits cyclooxygenase, resulting in inhibition of synthesis of prostaglandins and other inflammatory mediators.
Indications / Dosage / Route |
Routes of Administration: Oral, Topical (in the form of Gels and Sprays) and Ophthalmic.
Condition: Analgesia, Primary Dysmenorrhea
Dose: Adults – Oral (PO) 50 mg T.I.D (Three times in a day) – Max 150 mg / Day
Condition: Rheumatoid Arthritis
Dose: Adults – Oral (PO) 50 mg T.I.D or Q.I.D (4 times a day)
If the condition is chronic then use Extended Release Tablets 100 mg QD (once in a day) or B.I.D (Twice a day) – Max 225 mg / Day
Condition: Osteoarthritis
Dose: Adults – Oral (PO) 50 mg B.I.D or T.I.D
If the condition is chronic then use Extended Release Tablets, 100 mg / Day. Max: 200 mg / Day.
Condition: Ankylosing Spondylitis
Dose: Adults – Oral (PO) 25 mg Q.I.D (4 times in a Day). Max: 125 mg / Day.
Ophthalmic Solution:
Condition: Following cataract surgery
Dose: 0.1%, 1 drop in affected eye Q.I.D (4 times in a Day) – 24 hours after cataract surgery.
Adjustment of Dosage |
Kidney disease: None.
Liver disease: None.
Elderly: May be necessary to reduce dose for patients >65 years.
Pediatric: Safety and efficacy have not been established.
Food and Drug Interactions |
Food: Take with food or large quantities of water or milk.
Pregnancy: Category B. Category D in third trimester or near delivery.
Lactation: May appear in breast milk. Breastfeeding considered to be low risk by some authors.
Drug Interactions: Hypersensitivity and cross-sensitivity with other NSAIDs and aspirin.