This discussion includes the following information related to Cholecystitis:
- Cholecystitis
- Types of Cholecystitis
- Signs and Symptoms of Cholecystitis
- Causes of Cholecystitis
- Risk Factors for Cholecystitis
- Complications of Cholecystitis
- Tests and Diagnosis for Cholecystitis
- Treatment and Drugs for Cholecystitis
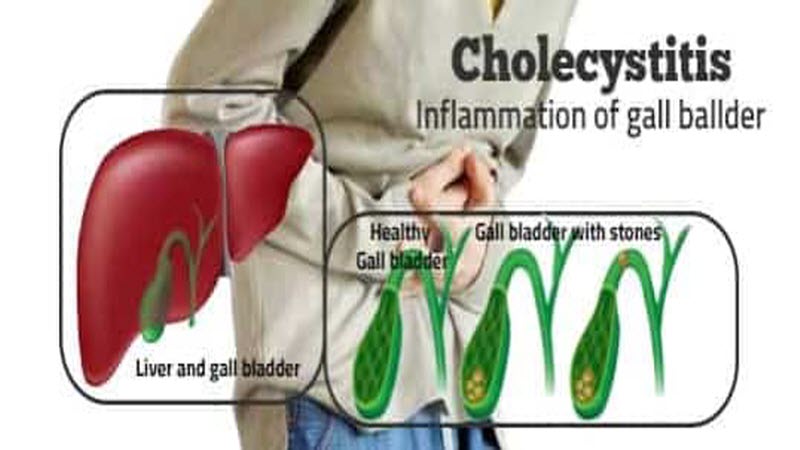
Cholecystitis Definition
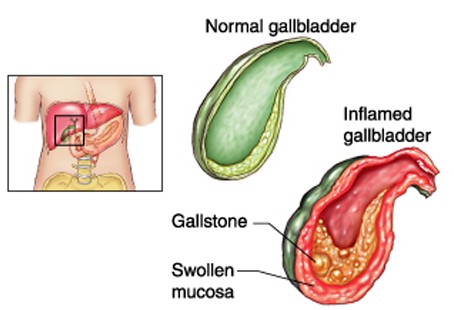
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, beneath your liver. The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid that’s released into your small intestine (bile).
In most cases, gallstones blocking the tube leading out of your gallbladder cause cholecystitis. This results in a bile buildup that can cause inflammation. Other causes of cholecystitis include bile duct problems and tumors.
If left untreated, cholecystitis can lead to serious, sometimes life-threatening complications, such as a gallbladder rupture. Treatment for cholecystitis often involves gallbladder removal.
Types of Cholecystitis
There are two types of Cholecystitis:
- Acute Cholecystitis: This is a sudden inflammation of the gallbladder and usually causes severe abdominal pain, often with nausea, vomiting, and fever. Pain is mostly localized between the shoulder blades. This condition requires immediate attention as it can be a life-threatening situation.
- Chronic Cholecystitis: When acute Cholecystitis persists for several months or years, it is known as Chronic Cholecystitis. Chronic Cholecystitis may not have any symptoms at all or may cause intermittent abdominal discomfort. This condition causes damage to the walls of the gallbladder causing it to become thickened and scarred. As a result the gallbladder may shrink in size and lose its ability to store and release bile properly.
Signs and Symptoms of Cholecystitis
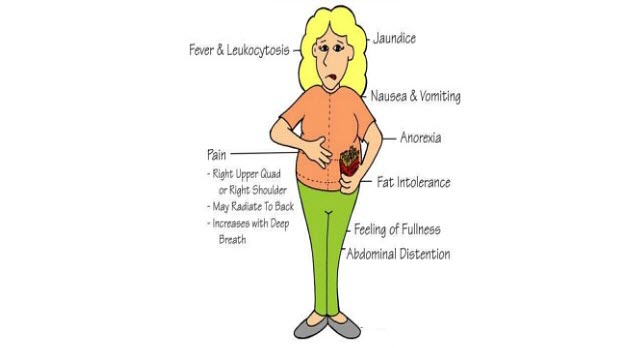
Signs and symptoms of cholecystitis may include:
- Severe pain in your upper right abdomen
- Pain that radiates from to your right shoulder or back
- Tenderness over your abdomen when it’s touched
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
Cholecystitis signs and symptoms often occur after a meal, particularly a large or fatty meal.
Causes of Cholecystitis
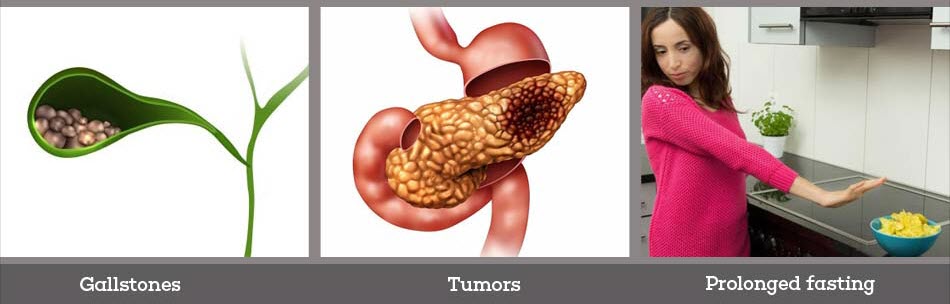
Cholecystitis occurs when your gallbladder becomes inflamed. Gallbladder inflammation can be caused by:
- Gallstones: Most cholecystitis is the result of hard particles that develop in your gallbladder (gallstones) from imbalances in the substances in bile, such as cholesterol and bile salts. Gallstones can block the cystic duct — the tube through which bile flows when it leaves the gallbladder — causing bile to build up and resulting in inflammation.
- Tumor: A tumor may prevent bile from draining out of your gallbladder properly, causing bile buildup that can lead to cholecystitis.
- Bile duct blockage: Kinking or scarring of the bile ducts can cause blockages that lead to cholecystitis.
Risk Factors for Cholecystitis
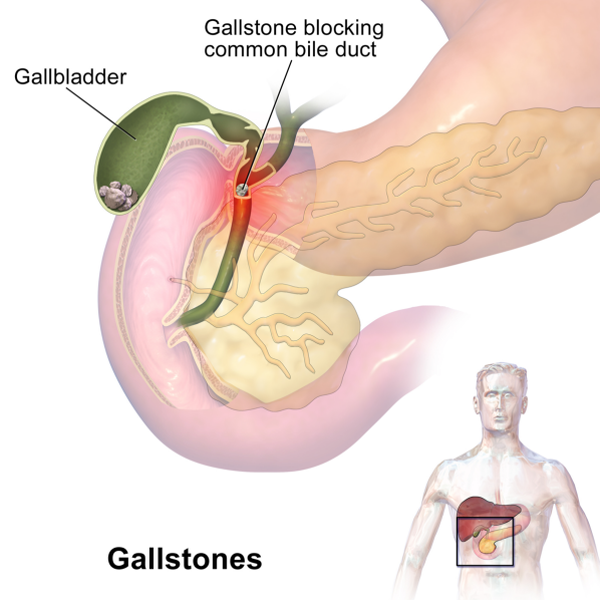
Having gallstones is the main risk factor for developing cholecystitis.
Complications of Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis can lead to a number of serious complications, including:
- Infection within the gallbladder: If bile builds up within your gallbladder, causing cholecystitis, the bile may become infected.
- Death of gallbladder tissue: Untreated cholecystitis can cause tissue in the gallbladder to die, which in turn can lead to a tear in the gallbladder, or it may cause your gallbladder to burst.
- Torn gallbladder: A tear in your gallbladder may result from gallbladder enlargement or infection.