Tetracycline is an antibiotic used to treat a number of infections. This includes acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is taken by mouth.
Molecular Structure |
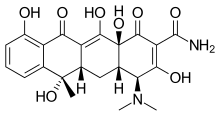
Class of Drug |
Tetracycline antibiotic.
Mechanism of Action |
Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis after specific ribosomal binding.
Susceptible organisms in vivo: Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia recurrentis. Brucella sp, Calymmatobacterium granulomatis, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Chlamydia psittaci, Chlamydia trachomatis, Ehrlichia sp, Helicobacter pylori, Rickettsia (Q fever), Rickettsia sp, Vibrio sp.
Indications / Dosage / Route |
Routes of Administration: Oral, IV and IM.
Condition: Usual dose
Dose: Adults: PO 1-2 g/d in 2 or 4 equal doses.
Children: >8 years: Daily dose is 10-20 mg/lb (25-50 mg/kg in 4 equal doses).
Condition: Brucellosis
Dose: PO 500 mg 4 times/d for 3 weeks, accompanied by 1 g streptomycin IM 2 times/d the first week and once daily the second week.
Condition: Syphilis
Dose: PO 30-40 g in equally divided doses over 10-15 days. Perform close follow-up and laboratory tests.
Condition: Uncomplicated urethral, endocervical, or rectal infections caused by C. trachomatis.
Dose: PO 500 mg 4 times/d for at least 7 days.
Condition: Severe acne
Dose: PO: Initial: 1 g/d in divided doses. Maintenance: 125-500 mg/d.
Condition: Lymphogranuloma venereum: genital, inguinal or anorectal
Dose: PO 500 mg 4 times/d for at least 2 weeks.
Condition: Nongonococcal urethritis
Dose: PO 500 mg 4 times/d for 7 days.
Condition: Acute pelvic inflammatory disease, ambulatory treatment
Dose: Adults: 2 g IM cefoxitin, 3 g oral amoxicillin, 3.5 g oral ampicillin, 4.8×106 units IM aqueous procaine penicillin G at 2 sites or 250 mg IM ceftriaxone. Each (except ceftriaxone) should be accompanied by 1 g oral probenecid. Follow with 500 mg tetracycline 4 times/d.
Children: >8 years: 150 mg/kg/d IV cefuroxime or 100 mg/kg/d IV ceftriaxone followed by 30 mg/kg/d IV tetracycline in 3 doses, continued for at least 4 days. Thereafter, continue tetracycline orally to complete at least 14 days of therapy.
Adjustment of Dosage |
Kidney disease: None.
Liver disease: None.
Elderly: None
Pediatric: Not to be used in children <8 years unless all other drugs are either ineffective or contraindicated.
Food and Drug Interactions |
Food: Take 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals. Dairy products interfere with tetracycline absorption.
Pregnancy: Category D.
Lactation: Appears in breast milk. Considered compatible by American Academy of Pediatrics.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to any tetracycline, patients with esophageal obstruction, children <8 years
Warnings / Precautions |
> Use with caution in patients with impaired kidney function.
> Administer IM by deep injection into large muscle. If injected inadvertently SC or into fat layer, severe pain may result. This can be relieved by means of an ice pack. IM solution should be used within 24 hours of preparation.
> The drug may permanently discolor (yellow brown to gray) deciduous or permanent teeth or cause enamel hypoplasia. Premature infants may experience decreased fibula growth.
> Do not administer antacids that contain calcium, aluminum, or magnesium.
Clinically Important Drug Interactions |
> Drugs that decrease effects/toxicity of tetracyclines: aluminum antacids, iron preparations, calcium salts, magnesium salts, sodium bicarbonate, zinc salts, bismuth salts, cimetidine.
> Tetracyclines increase effects/toxicity of oral anticoagulants, bumetanide, digoxin, thiazide diuretics, ethacrynic acid, furose- mide, insulin, methoxyflurane.
> Tetracyclines decrease effects/toxicity of penicillins.
Adverse Reactions |
> Common: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia.
> Serious: renal toxicity, hypersensitivity reactions, benign intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri), pericardits, diabetes insipidus, pseudomembranous colitis, hepatitis, anaphylaxis
Parameters to Monitor |
> Serum BUN and creatinine, liver enzymes.
> Signs of possible oliguria, which may result in accumulation of the drug.
> Signs and symptoms of pseudotumor cerebri in adults: headaches, diplopia.
> Signs and symptoms of pseudomembraneous colitis: Discontinue drug if possible. If necessary, treat with vancomycin, metronidazole, and cholestyramine.
> Signs and symptoms of phlebitis from IV injections.
> Renal function in patients with preexisting renal impairment. If indicated, monitor serum drug levels. Maintain level below 15 p,g/mL.
> Serum enzymes in patients with preexisting kidney or liver disease or those receiving concomitant hepatotoxic drug.
Advice to Patient |
> Discard drug if it is beyond expiration date. Outdated drug can cause severe kidney toxicity (Fanconi-like syndrome).
> To minimize possible photosensitivity reaction, apply adequate sunscreen and use proper covering when exposed to strong sunlight.
> Store drug away from light, heat, and high humidity.
> Use two forms of birth control including hormonal and barrier methods.
> Do not take drug at bedtime.
Further Useful Info |
> Uses for tetracyclines include treatment of early Lyme disease, Vibrio infections such as cholera, and rickettsial infections including typhus, Q fever, and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. They are also used to treat genital infections (granuloma ing¬uinale, nongonococcal urethritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and other infections caused by C. trachomatis).



