Rofecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that has now been withdrawn over safety concerns. It was marketed by Merck & Co. to treat osteoarthritis, acute pain conditions, and dysmenorrhea.
Molecular Structure |
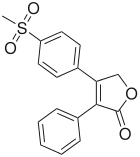
Class of Drug |
Antiinflammatory, analgesic, COX-2 inhibitor
Mechanism of Action |
Selective inhibitor of COX-2, the enzyme required for synthesis of prostaglandins and other products of the arachidonic acid cascade.
Indications / Dosage / Route |
Routes of Administration: Oral only.
Condition: Osteoarthritis
Dose: Adults: 12.5-25 mg/d.
Condition: Analgesia
Dose: Adults: 25-50 mg/d. Maximum: 5 days..
Adjustment of Dosage |
Kidney disease: None. Potentially toxic to kidney
Liver disease: Reduce dosage. Monitor carefully.
Elderly: Use lowest recommended dose.
Pediatric: Safety and efficacy have not been determined in children <18 years.
Food and Drug Interactions |
Food: May be taken with or without food
Pregnancy: Category C. Category D in third trimester and near delivery.
Lactation: No data available. Best to avoid.
Contraindications: Severe liver disease, history of allergic reaction to aspirin or other NSAIDs, hypersensitivity to rofecoxib.
Warnings / Precautions |
> Use with caution in patients with active gastric ulcer, history of ulcer disease or GI bleeding, active asthma, hypertension, fluid retention, chronic kidney or liver disease.
> Rofecoxib can cause significant GI bleeding despite being a specific COX-2 inhibitor.
> Potentially toxic to kidneys, particularly when prostaglandins maintain renal blood flow (renal and heptatic insufficiency, CHF).
Clinically Important Drug Interactions |
> Drugs that increase effects/toxicity of rofecoxib: rifampin, other P450 inhibitors, aspirin.
> Drugs that decrease effects/toxicity of rofecoxib: antacids.
> Rofecoxib increases effects/toxicity of methotrexate, warfarin, lithium.
> Rofecoxib decreases effects/toxicity of furosemide, thiazide diuretics
Adverse Reactions |
> Common: None.
> Serious: GI bleeding, arrhythmias, allergic reactions.
Parameters to Monitor |
> Improvement in pain and inflammation.
> Signs and symptoms of salt and water retention.
> Signs and symptoms of GI toxicity.
> Signs and symptoms of renal toxicity.
Advice to Patient |
> Report to treating physician if you experience dyspepsia, changes in stool, abdominal pain, or swelling of ankles.
Further Useful Info |
> In limited studies, rofecoxib is as effective as other NSAIDs in osteoarthritis and has a lower incidence of GI toxicity than the older drugs. However, the incidence of long term GI effects has not been determined as compared with NSAIDs or other COX-2 inhibitors. Future uses of Cox-2 inhibitors may include chemoprevention of colonic neoplasms.



